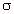 = =
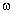
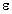 o
o
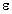 " " |
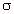 is conductivity in siemens/meter is conductivity in siemens/meter |
|
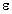 o = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m: permittivitiy of free space o = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m: permittivitiy of free space |
| 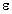 " is the imaginary part of complex relative permittivity " is the imaginary part of complex relative permittivity |
| |
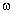 = 2
= 2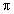 f f | 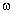 is radian frequency in radians/second
is radian frequency in radians/second |
| f is frequency in hertz |
| |
tan 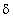 = = 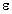 "/ "/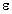 ' ' | tan 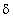 is the loss tangent is the loss tangent |
| |
P = 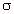 | E |2 | E |2 |
P is density of absorbed power at a point in watts/cubic meter |
| 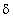 is conductivity in siemens/meter at the point is conductivity in siemens/meter at the point |
| |E | is rms electric-field intensity in rms volts/meter |
| |
D = 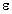 E E | D is electric-flux density in coulombs/square meter |
| 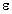 is permittivity in farads/meter is permittivity in farads/meter |
| E is electric-field intensity in volts/meter |
| |
B = 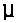 H H | B is magnetic-flux density in tesla |
| 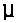 is permeability in henry/meter is permeability in henry/meter |
| H is magnetic-field intensity in amperes/meter |
| |
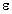 o=8.85 x 10-12 F/m o=8.85 x 10-12 F/m | 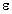 o is the permittivity of free space o is the permittivity of free space |
| |
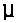 o = 4 o = 4 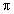 x 10-7 H/m x 10-7 H/m | 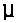 o is the permeability of free space o is the permeability of free space |
| |
| f = 1/T | f is frequency in hertz |
| |
| T is period in seconds |
| |
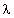 = v/f = v/f | 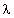 is wavelength in meters is wavelength in meters |
| |
| v is velocity of propagation in meters/second |
| f is frequency in hertz |
| |
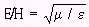 | E/H is the wave impedance in ohms |
| E/H = 377 ohms in free space | E is the magnitude of the electric-field intensity in volts/meter |
| H is the magnitude of the magnetic-field intensity in amperes/meter |
| |
| |
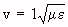 | v is the velocity of propagation in meters/second |
| v = 3 x 108 m/s in free space | 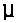 is the premeability in henry/meter is the premeability in henry/meter |
| 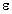 is the permittivity in farad/meter is the permittivity in farad/meter |
| |
| <P> = <E x H> | <P> is the time-averaged Poynting's vector in watts/square meter |
| E is the electric-field intensity in rms volts/meter |
| H is the magnetic-field intensity in rms amperes/meter |
| |
| P = E2/377 | P is the magnitude of the time-average Poynting vector for a planewave in free space |
| E is the magnitude of the electric-field intensity in rms volts/meter |
| 377 is the wave impedance of free space in ohms |
| |
| S = Emax/Emin | S is the standing-wave ratio (unitless) |
| E max is the maximum value of the magnitude of the electric-field intensity anywhere along the wave |
| E min is the minimum value of the magnitude of the electric-field intensity anywhere along the wave |
| |
S = (1 + 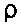 ) / (1 - ) / (1 - 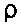 ) ) | S is the standing-wave ratio (unitless) |
| 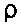 is the magnitude of the reflection coefficient (ratio of reflected E-field to incident E-field)
is the magnitude of the reflection coefficient (ratio of reflected E-field to incident E-field) |
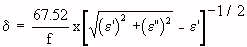 | |
| 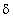 is the skin depth in meters is the skin depth in meters |
| 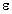 ' is the real part of the permittivity ' is the real part of the permittivity |
| 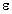 " is the imaginary part of the permittivity
" is the imaginary part of the permittivity |
| f is the frequency in MHz |
| |
SAR =
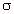 |E| 2 / |E| 2 / 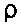 m m | SAR is the local specific absorption rate in watts/kilogram |
| 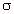 is the conductivity in siemens/meter is the conductivity in siemens/meter |
| |E| is the electric-field strength in rms volts/meter |
| 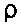 m is the mass density in kilograms/cubic meter m is the mass density in kilograms/cubic meter |
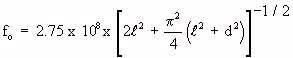 | |
| fo is the resonant frequency in hertz of the SAR for E polarization |
| 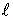 is the average length of the absorbing object is the average length of the absorbing object |
| d is the average diameter of the absorbing object |
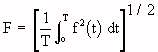 | F is the rms value of the periodic function f (t) |
| T is the period of the function |
| |
G = gp /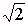 | G is the rms value of a sinusoid |
| Gp is the peak value of the sinusoid |
| |
d = 2L2/
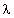 | d is the approximate distance from an antenna at which the n ear fields become negligible and the fields are approximately far fields |
| L is the largest dimension of the antenna |
| 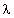 is the wavelength is the wavelength |
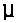 is permeability in henry/meter
is permeability in henry/meter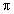 x 10-7 H/m
x 10-7 H/m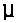 o is the permeability of free space
o is the permeability of free space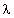 = v/f
= v/f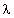 is wavelength in meters
is wavelength in meters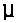 is the premeability in henry/meter
is the premeability in henry/meter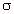 |E| 2 /
|E| 2 / 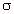 is the conductivity in siemens/meter
is the conductivity in siemens/meter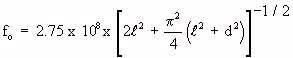
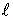 is the average length of the absorbing object
is the average length of the absorbing object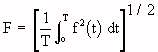
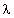
 is the wavelength
is the wavelength