Session 3 - 6
STUDIES ON BIO-SENSING MICROSYSTEMS FOR HEALTH CARE
Eiji Takeda, Takashi Handa, Shuichi Shoji, Akihiko Uchiyama
Waseda Univ. Dep. of Electrical and Communication Engineering
3-4-1 Ohkubo, Shinjuku-ward, Tokyo, JAPAN 169
INTRODUCTION A Micro-Capsule (MC) for measuring pressure, temperature, and pH in digestive tract, and a very low-powered consumption wireless ECG (Electrical Cardio Gram) sensing system is studied in order to realize real time monitoring for health care.
MICRO-CAPSULE The capsule including a glass pH sensor, a transmitter and a button battery was already presented.* To achieve miniaturization for this capsule, we applied micro-machining to fabricate a silicon based multi-sensor of pressure, temperature, pH. A piezo resistive diaphragm pressure sensor (1.8 x 1.8 mm2), a p-n junction temperature sensor (0.5 x 1 mm2), and a Si3N4 gate pH ISFET (0.2 x 0.6 mm2) are fabricated on a 4.2 x 2.8 x 0.2 mm3 silicon wafer as shown in Fig.1.
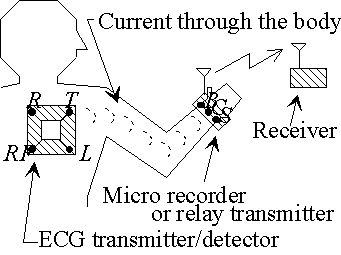
ECG SYSTEM The schematic of an ECG monitoring system is shown in Fig.2. The ECG detector/transmitter, located on the chest, has three detection electrodes (R,L,RF), and an electrode for signal transmission (T). The detected ECG is amplified and modulated, then applied between electrodes T and RF. The signal is turned into AC micro current and can be transmitted through the body. It is then detected by the relay transmitter placed on the wrist that has three detection electrodes. The power necessary for this transmission is only 8µW (400mVRMS x 20µARMS), and can be driven by a very small battery. This concept is useful for multi-monitoring of health parameters because each detector part should not have its own RF transmitter so as to minimize the electromagnetic noise problems and to achieve low power consumption.
*K. Saito, A. Uchiyama, et. al. 12th Int. Symp. Biotelemetry, pp415-419, 1992
